Implantable medical devices including cardiac pacemakers and brain pacemakers are increasingly prevalent, although replacing their batteries surgically is a drawback for long-term functionality and patient health. Current devices are also large and rigid, with potential discomfort to the patient post-implantation. To address this problem, Peng Jin and a research team in mechanics and electronics in Beijing China, developed a thin, battery-free and flexible implantable system for wireless recharging and communication via ultrasound. The results automatically determined abnormal heartbeats and responded by simulating the heart electrically to demonstrate the potential of the device for emerging treatments.
Medical devices for power transfer
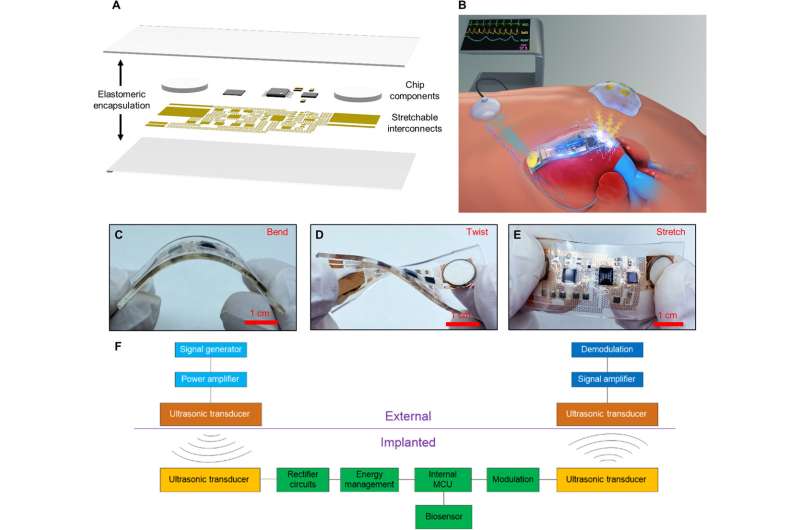
Implantable electronic equipment (IEE) is vital in the medical field to perform drug delivery and physiological parameter monitoring as cardiac and brain pacemakers. Implantable glucose sensors can also provide accurate, real-time glucose monitoring to assist diabetic individuals. The applications of IEE are, however, held back by shortcomings of the batteries used. A possible solution is the adoption of an implantable fuel system using endogenous substances such as glucose to create electricity via an electrochemical reaction. The power transfer method can be delivered wirelessly through tissue. To accomplish an optimal setup exceeding conventional methods of wireless power transfer and communication, Jin et al. developed an implantable acoustic energy transfer and communication device (AECD). The flexible electronic technology-based device was soft, comfortable and well-adapted to the human biological structure, as a stretchable ultrasonic device for ultrasonic energy transfer and efficient communication.
Device design
To build the AECD, the scientists incorporated a fractal serpentine copper pattern placed on a polyimide pattern layer, where the circuit interconnected between chip components. The researchers encapsulated all the components in a soft polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) layer to make the AECD soft, flexible, and accommodating without altering its function. They verified the flexibility of the device with repeated mechanical testing to minimize the damage and inflammatory response in the human body after implantation. The entire system achieved wireless energy transfer and wireless communication via ultrasound. To achieve this, the team integrated five modules and upon implantation, the AECD ultrasonic transducer accepted the ultrasound transmitted by the rectifier module and the energy management module to power the control unit. After activation, the unit collected physiological information via biosensors to then transmit information-coded ultrasound, which an external ultrasound system then received to recover the physiological information. For example, the AECD functioned as an implantable heart monitoring device to wirelessly monitor the heart’s health via ultrasound.
Developmental process
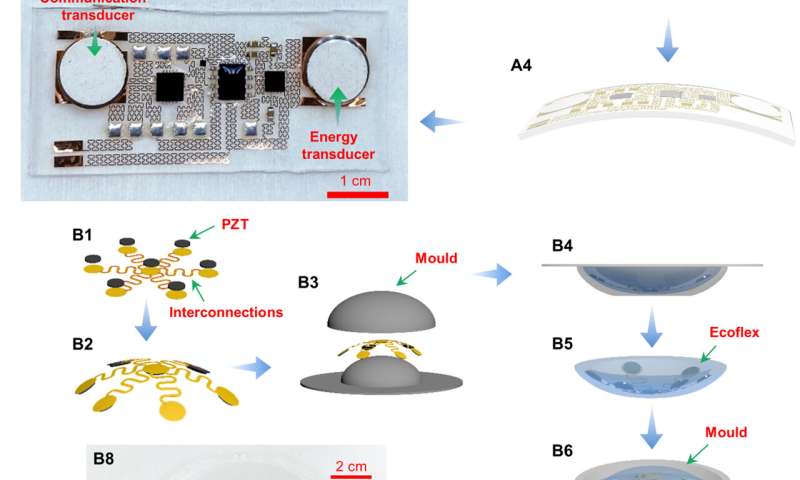
To build the AECD, Jin et al. used a two-step manufacturing process: First, they established the circuit and then packaged it. The researchers also specially designed external energy-transmitting equipment to transmit ultrasound and provide energy to the acoustic energy transfer and communication device (AECD). The entire process of AECD manufacture included a three-step process. The next process of external energy-transmitting equipment (EETE) development comprised of an array of ultrasonic transducers and the implantation of the completed device into a flexible base. Jin et al. then created the ultrasonic array using an ultrathin, flexible, printed circuit produced using an identical flexible printed circuit technology.
Wireless energy transfer
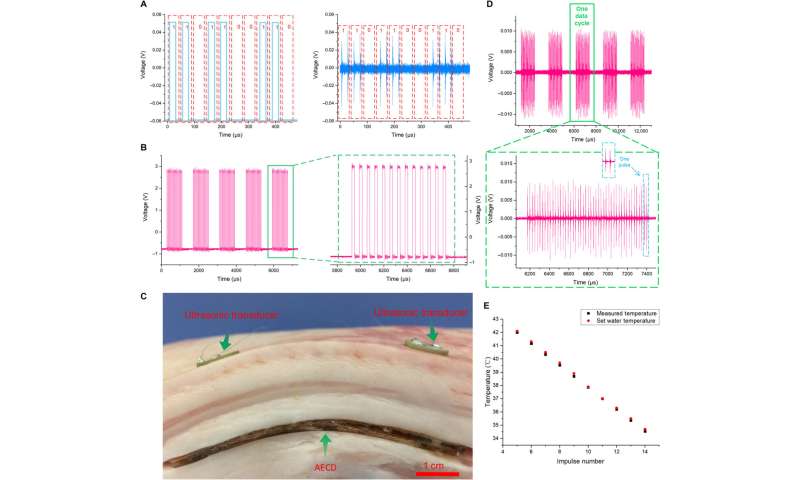
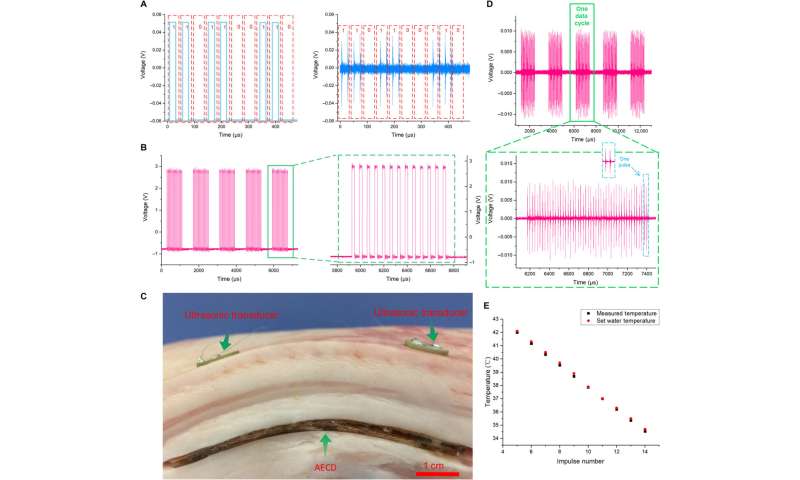
The researchers achieved wireless power transfer via an acoustic method by converting mechanical to electrical energy. To achieve this, they transmitted ultrasound to the AECD receiver in vitro, then the AECD ultrasonic accepted the ultrasound and converted it to electrical energy in vivo. The AECD energy management then supplied energy to the entire internal electronic system. The scientists used many small transducers in an array to prevent acoustic scattering for efficient power transfer and developed a centralized symmetric curved design to focus ultrasound on a specific point in the central line and implanted it in a flexible base made of silicone. They then developed a centralized symmetric curved design to focus ultrasound on a specific point in the central line and implanted it in a flexible base made of silicon and confirmed the feasibility of the proposed method using acoustic simulations.
Wireless communication
Using the acoustic energy transfer and communication device (AECD), Jin et al. transmitted information-coded ultrasound to achieve ultrasound-based wireless communication. In its working state, a biological sensor acquired physiological information and then regulated the information into the corresponding pulse signal. Simultaneously, an external ultrasonic transducer accepted the ultrasound and converted it to a voltage signal. The team then demodulated and recovered the voltage signal undergoing amplification and filtration to recover it via a computer to obtain internal physiological information. Thereafter they facilitated wireless acoustic communication using a special signal modulation and demodulation technique. The team conducted experiments to directly show the function of the AECD during simultaneous acoustic energy transfer and communication in biological environments using a piece of fresh meat and a water heating device to measure their inherent temperatures using the described method.
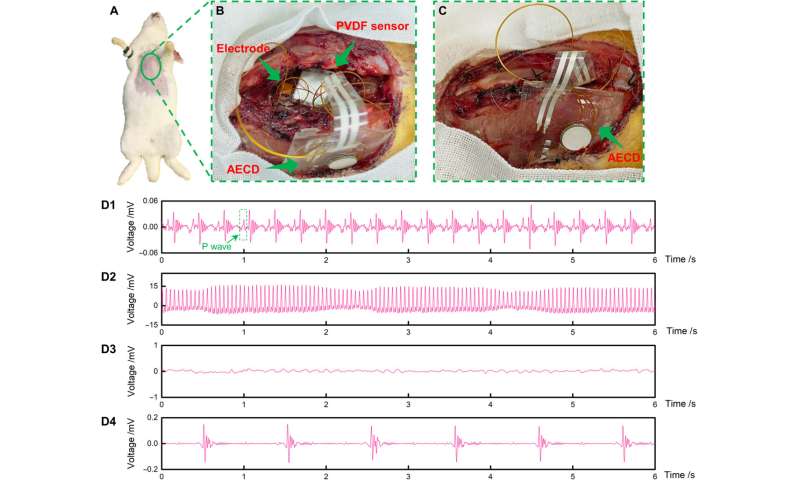
Cardiac pacing experiments and outlook
The versatile implantable electronic equipment device developed in this work functioned in many areas as a heart pacemaker and nerve stimulator. As proof-of-concept, Jin et al. conducted a cardiac pacing experiment with a rabbit animal model. During the experiment, they implanted the AECD inside the subcutaneous tissue of a rabbit’s chest and recorded the electrocardiogram (ECG) and monitored the heartbeat to indicate the normal heart rhythm of the rabbit. The device also indicated its capacity to detect abnormal heartbeats.
Source: Read Full Article
