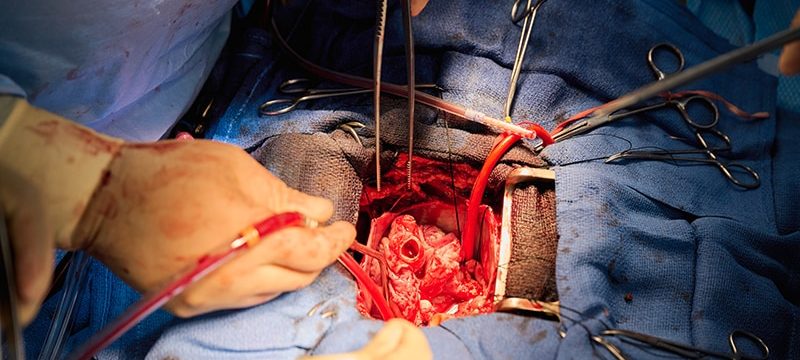
A team of surgeons successfully transplanted genetically engineered pig hearts into two recently deceased people whose bodies were being maintained on ventilatory support – not in the hope of restoring life, but as a proof-of-concept experiment in xenotransplantation that could eventually help to ease the critical shortage of donor organs.
The surgeries were performed on June 16 and July 6, 2022, using porcine hearts from animals genetically engineered to prevent organ rejection and promote adaptive immunity by human recipients
“From the very beginning our goal was to be able to create a model where we actually mimicked what is now done clinically in human transplantation, without utilizing unapproved devices or techniques or medications,” said Nader Moazami, MD, surgical director of heart transplantation and chief of the division of heart and lung transplantation and mechanical circulatory support at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Through 72 hours of postoperative monitoring “we evaluated the heart for functionality and the heart function was completely normal with excellent contractility,” he said at a press briefing announcing early results of the experimental program.
He acknowledged that for the first of the two procedures some surgical modification of the pig heart was required, primarily because of size differences between the donor and recipient.
“Nevertheless, we learned a tremendous amount from the first operation, and when that experience was translated into the second operation it even performed better,” he said.
Alex Reyentovich, MD, medical director of heart transplantation and director of the NYU Langone advanced heart failure program noted that “there are 6 million individuals with heart failure in the United States. About 100,000 of those individuals have end-stage heart failure, and we only do about 3,500 heart transplants a year in the United States, so we have a tremendous deficiency in organs, and there are many people dying waiting for a heart.”
Infectious Protocols
To date there has been only one xenotransplant of a genetically modified pig heart into a living human recipient, David Bennett Sr., age 57. The surgery, performed at the University of Maryland in January 2022, was initially successful, with the patient able to sit up in bed a few days after the procedure, and the heart performing like a “rock star” according to transplant surgeon Bartley Griffith, MD.
However, Bennett died 2 months after the procedure from compromise of the organ by an as-yet undetermined cause, of which one may have been the heart’s infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (CMV).
A genetically modified pig heart suspended in solution ahead of xenotransplantation at NYU Langone Health on July 6, 2022, in New York.
The NYU team, mindful of this potential setback, used more sensitive assays to screen the donor organs for porcine CMV, and implemented protocols to prevent and to monitor for potential zoonotic transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus.
The procedure used a dedicated operating room and equipment that will not be used for clinical procedures, the team emphasized.
The hearts were taken from pigs genetically modified with knockouts of four porcine genes to prevent rejection — including a gene for a growth hormone that would otherwise cause the heart to continue to expand in the recipient’s chest — and with the addition of six human transgenes encoding for expression of proteins regulating biologic pathways that might be disrupted by incompatibilities across species.
Vietnam Veteran
The organ recipients were recently deceased patients who had expressed the clear wish to be organ donors but whose organs were for clinical reasons unsuitable for transplant.
The first recipient was Lawrence Kelly, a Vietnam War veteran and welder who died from heart failure at the age of 72.
“He was an organ donor, and would be so happy to know how much his contribution to this research will help people like him with this heart disease. He was a hero his whole life, and he went out a hero,” said Alice Michael, Kelly’s partner of 33 years, who also spoke at the briefing.
“It was, I think, one of the most incredible things to see a pig heart pounding away and beating inside the chest of a human being,” said Robert A. Montgomery, MD, DPhil, director of the NYU Transplant Institute, and himself a heart transplant recipient.
This article originally appeared on MDEdge.com.
For more from theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, follow us on Twitter and Facebook.
Source: Read Full Article